1. Introduction to Generative AI
Generative AI represents a paradigm shift in artificial intelligence, enabling machines to create original content such as text, images, music, and even code. Unlike traditional AI, which primarily analyzes data to make predictions or classifications, generative AI produces novel outputs that mimic human creativity, often indistinguishable from human-made work.
In 2025, generative AI is at the forefront of technological innovation, driven by breakthroughs in machine learning, increased computational power, and vast datasets. From its early days with basic text generation models, it has evolved into sophisticated systems capable of complex reasoning and autonomous decision-making.

This article delves into the journey of generative AI, tracing its progression from assistive tools like AI copilots to advanced reasoning agents. It examines the technologies, applications, challenges, and societal impacts shaping its trajectory, offering a comprehensive look at its role in 2025 and beyond.
The significance of generative AI lies in its ability to augment human capabilities while raising critical questions about ethics, employment, and privacy. Understanding its evolution is key to navigating its future.
2. The Rise of AI Copilots
AI copilots emerged in the early 2020s as assistive tools designed to enhance human productivity across various domains. Built on large language models, these systems provide real-time suggestions, automate repetitive tasks, and streamline workflows, acting as virtual collaborators.

The strength of copilots lies in their ability to process natural language and deliver tailored outputs, making them accessible to non-experts. For instance, a developer can write complex code faster, while a writer can refine drafts with AI-generated suggestions.
However, copilots are inherently reactive, limited to providing assistance within predefined tasks. They lack the capacity for independent problem-solving or multi-step reasoning, which has spurred the development of more advanced AI systems.
By 2023, tools like GitHub Copilot for coding, Microsoft 365 Copilot for office tasks, and Adobe’s AI assistants for design had become integral to professional environments. These copilots excel at understanding context, generating relevant code snippets, drafting emails, or suggesting design elements based on user inputs.
3. Evolution to Reasoning Agents
Reasoning agents mark a significant leap in generative AI, transitioning from passive assistance to active decision-making. These agents can analyze complex scenarios, plan multi-step processes, and execute tasks autonomously, closely resembling human cognitive abilities.
In 2025, reasoning agents are deployed in scenarios requiring strategic thinking, such as optimizing supply chains, conducting scientific research, or managing financial portfolios. Unlike copilots, they can break down problems, evaluate options, and implement solutions without constant human oversight.
This evolution is enabled by advancements in neural architectures, such as enhanced transformer models, and techniques like reinforcement learning, which allow agents to learn from feedback and refine their decision-making processes.
The shift to reasoning agents is reshaping industries by enabling automation at a higher cognitive level, but it also introduces challenges related to control, accountability, and ensuring alignment with human values.
4. Key Technologies Powering Generative AI
At the core of generative AI are transformer models, which excel at processing sequential data like text and images. These models, trained on massive datasets, enable AI to generate coherent and contextually relevant outputs.
Diffusion models have revolutionized image and video generation, producing high-quality visuals used in gaming, film, and advertising. Meanwhile, reinforcement learning enhances AI’s ability to make decisions in dynamic environments, critical for reasoning agents.
Hardware advancements, including graphics processing units (GPUs), tensor processing units (TPUs), and neuromorphic chips, provide the computational power needed to train and deploy these models. Cloud computing further democratizes access to these resources.
Emerging techniques, such as few-shot learning and transfer learning, reduce the data and time required for training, making generative AI more efficient and adaptable to new tasks.
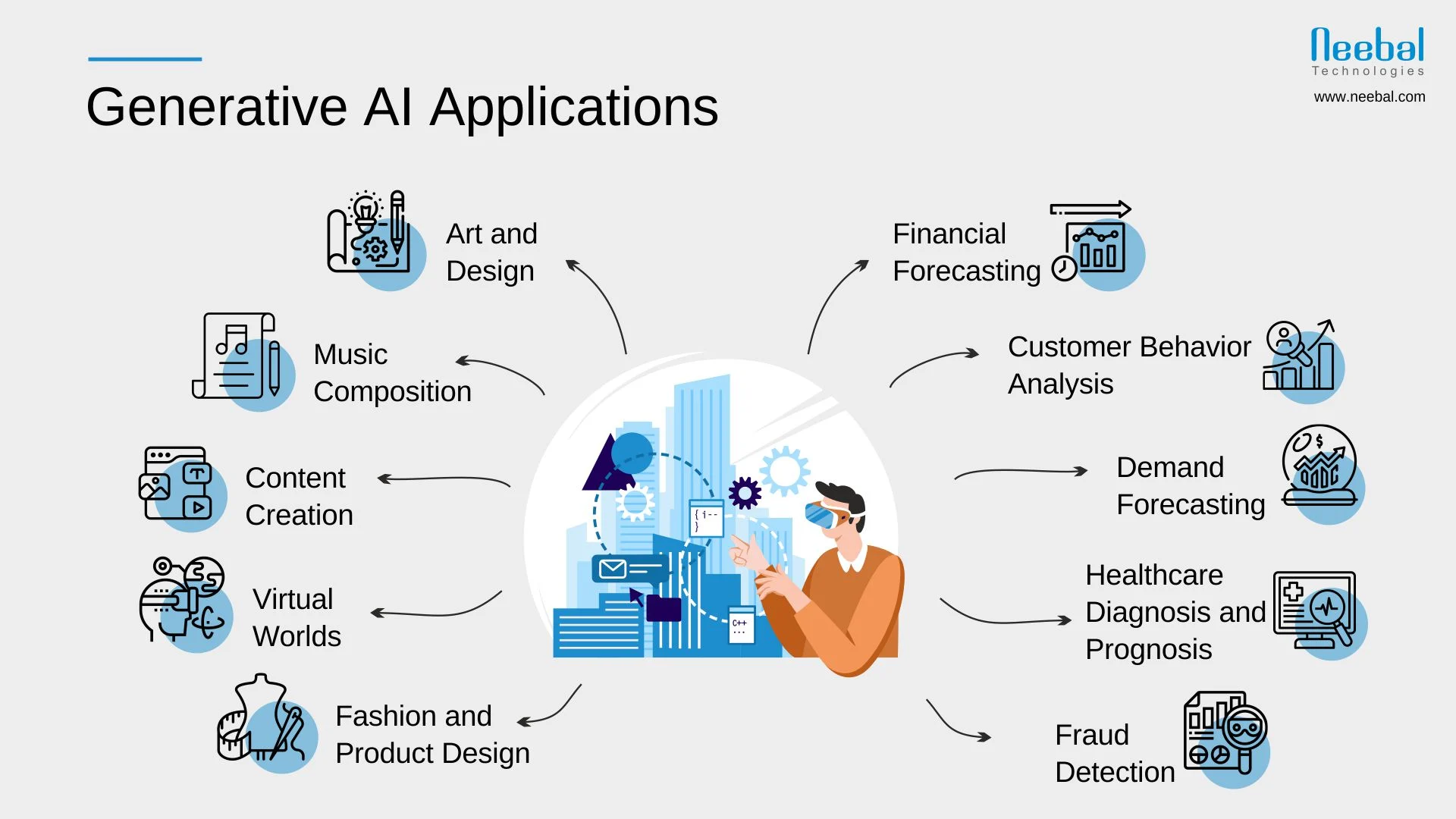
5. Applications Across Industries
In healthcare, generative AI accelerates drug discovery by designing molecules and predicting their efficacy. It also personalizes treatment plans by analyzing patient data, improving outcomes.
The entertainment industry leverages AI to create immersive experiences, from generating scripts and music to designing virtual worlds for gaming and the metaverse. AI-driven content is increasingly indistinguishable from human creations.
Businesses use generative AI for marketing, crafting personalized campaigns, and optimizing customer service through advanced chatbots. In manufacturing, AI enhances predictive maintenance, reducing downtime, and streamlines supply chain logistics.
In education, AI-powered tools deliver tailored learning experiences, adapting content to individual student needs and improving engagement and retention.
6. Ethical and Societal Implications
Generative AI’s ability to produce realistic content raises concerns about misinformation, as deepfakes and fabricated texts can spread rapidly. Robust detection mechanisms and regulatory frameworks are essential to mitigate these risks.
Job displacement is a pressing issue, as automation threatens roles in writing, design, and other creative fields. Reskilling programs and policies to support workforce transitions are critical to address this challenge.
Privacy concerns arise from AI’s reliance on large datasets, which may include sensitive personal information. Ensuring data anonymization and compliance with regulations like GDPR is vital.
Bias in AI models, inherited from training data, can perpetuate inequalities. Developers must prioritize fairness and inclusivity in model design to prevent harm.
7. Challenges in Development
Developing generative AI is resource-intensive, requiring substantial computational power and energy. The environmental impact of training large models is a growing concern, pushing research toward energy-efficient algorithms.
Model biases remain a challenge, as datasets often reflect societal prejudices. Rigorous testing and bias mitigation strategies are necessary to ensure equitable outcomes.
Scalability is another hurdle, as deploying AI at scale demands robust infrastructure, reliable maintenance, and seamless integration with existing systems.
Ensuring AI safety, particularly for reasoning agents, is critical. Misaligned objectives or unintended behaviors could lead to harmful consequences, necessitating strict oversight.
8. The Role of Data in AI Advancement
Data is the lifeblood of generative AI, fueling model training and performance. High-quality, diverse datasets enable AI to generate accurate and relevant outputs.
In 2025, synthetic data plays a growing role, addressing privacy concerns by generating artificial datasets that mimic real-world patterns without compromising sensitive information.

Data curation is a challenge, as poor-quality or biased data can degrade model performance. Automated tools for data cleaning and validation are becoming essential.
Access to data is also a barrier, as proprietary datasets limit innovation. Open-source initiatives and collaborative data-sharing frameworks are emerging to address this issue.
9. Future Prospects for 2025 and Beyond
By 2025, generative AI is expected to integrate seamlessly into daily life, with reasoning agents powering smart homes, autonomous vehicles, and personalized assistants.
Advancements in multimodal AI, combining text, image, and audio processing, will enable more versatile applications, from creative arts to scientific discovery.
Global collaboration on AI governance will shape its future, balancing innovation with ethical considerations. International standards for AI safety and fairness are likely to emerge.
Long-term, generative AI could redefine human-machine collaboration, augmenting creativity and problem-solving while addressing global challenges like climate change and healthcare access.
10. Conclusion
Generative AI has evolved from simple content generation to sophisticated reasoning agents, reshaping industries and society in 2025. Its journey from copilots to autonomous systems reflects remarkable technological progress.
While its applications are vast, from healthcare to entertainment, challenges like ethics, bias, and resource demands require careful navigation. The future of generative AI depends on responsible development and inclusive policies.
As we move forward, generative AI promises to augment human potential, but its success hinges on balancing innovation with accountability. The next decade will define its legacy.
“The future of generative AI lies in mastering data’s power, guiding us from copilots to reasoning agents with wisdom and responsibility.” — Elon Musk




































